flowchart TB PSUR --> Popularity[Use and sales<br>popularity] --> Rank((Rank<br>candidates)) Poll((Poll<br>categorical<br>cooperators)) --> CategList[Categorical<br>use list] DEC[DEC nominees] --> Unify((Unify<br>candidate<br>list)) CategList --> Unify Old[Our older list] --> Suffolk[Suffolk additions] --> Unify Unify --> Candidates MP[Hertfordshire and USDA<br>Mobility and persistence<br>databases] --> Rank Candidates --> Rank --> Top[Top candidates] Top --> Screen((Screen<br>lab capability<br>and workload)) Lab[Lab capabilities] --> Screen --> Final[Final list]
This is a page at Level 2 in the tree-level web, elaborating on analyte selection in its parent page at Level 1.
Navigate: ▲ 2: Sites and protocols
2.2 Analyte selection (Level 2)
Sales data provide hundreds of candidate active ingredient analytes. The lab can also test for environmental breakdown products (metabolites) of certain popular active ingredients.
The New York State Pesticide Sales and Use Reporting system (URL: https://dec.ny.gov/environmental-protection/pesticides/pesticide-reporting-law) established in 1996 requires reporting by pesticide users and sellers how much pesticide of what kind was used where, for restricted use products.
There were 600 different restricted-use pesticide active ingredients reported in 2022 as used by commercial pesticide applicators or sold to farmers (who do not have to report their own use). The top few (Figure 1) should be familiar, including glyphosate, atrazine, metolachlor, mineral oil, and sodium hypochlorite.
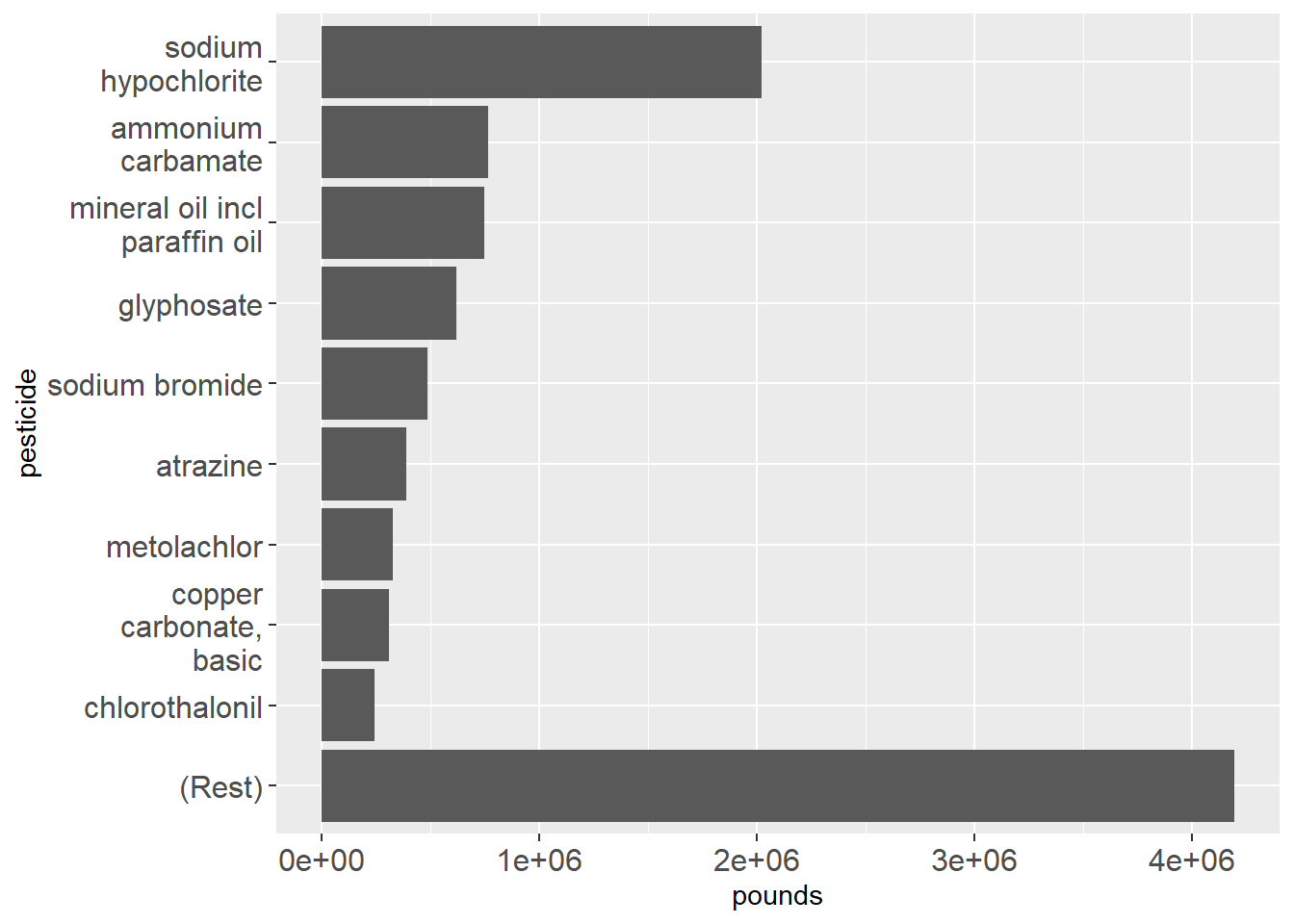
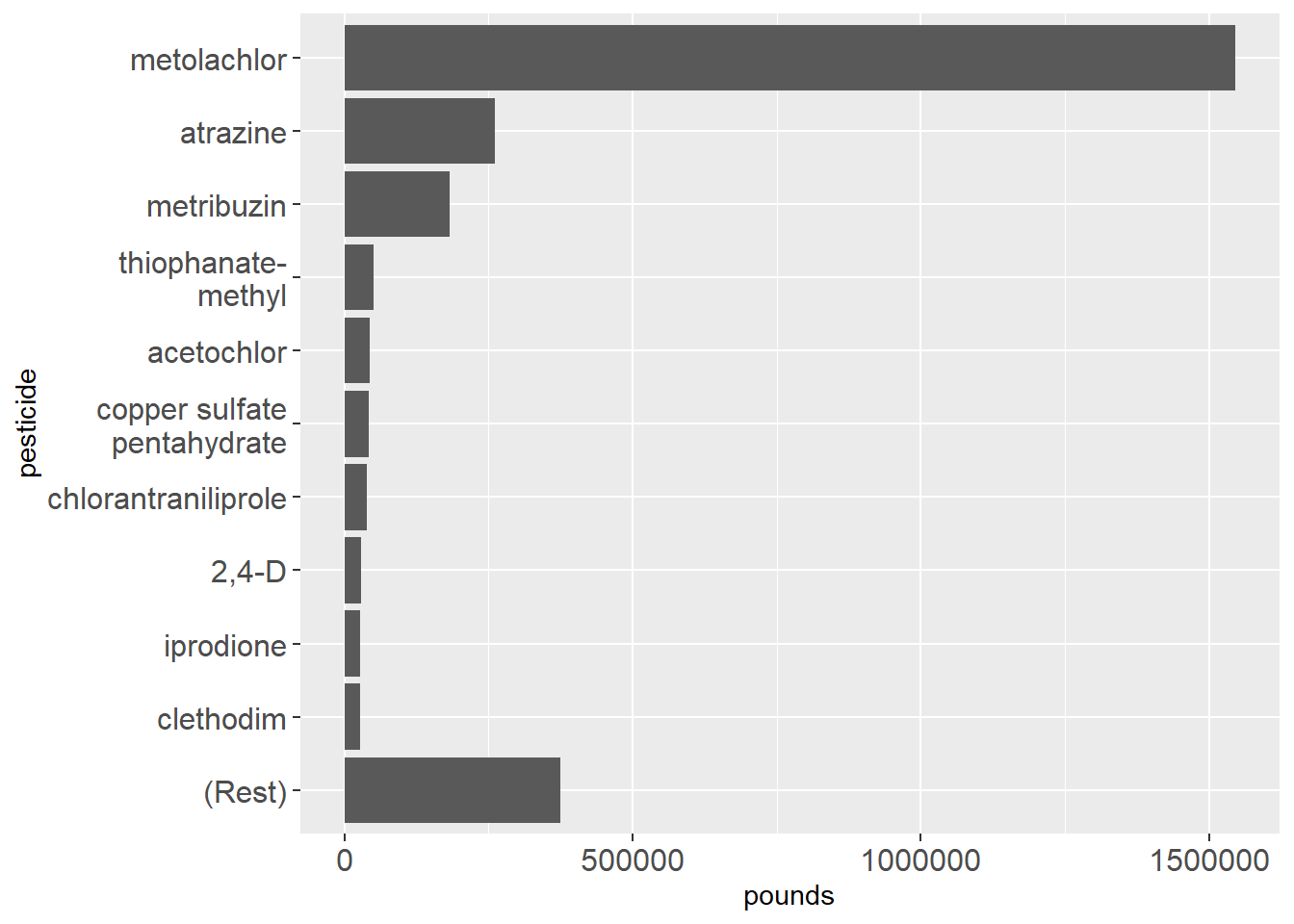
Data source: URL: https://dec.ny.gov/environmental-protection/pesticides/pesticide-reporting-law
Because the categorical type of site was most important to NYSDEC (expressed in target sample counts), we began considering candidate analytes by polling the early categorical cooperators for the products they used. The union of product lists from the early cooperators was the most important input to analyte choice for this project. Suffolk County Department of Health Services had nominated analytes also. We had an “old Cornell” list from earlier projects that had focused on field crop herbicides, last refined for use in lake sampling projects that had watersheds and adjacent land uses more residential than dairy agricultural. The old Cornell and Suffolk lists could be useful for the long term sites and lake sites of the project, and perhaps for upgradient sampling points at the categorical sites. Finally, DEC nominated certain analytes, in particular neonicotinoid compounds which are the subject of revised controls to protect pollinating insects. Figure 2 shows how we wove together these four sources into a list of candidate analytes for the lab.
Because lakes had an under 5% share of the annual samples target, we did not stress pesticide transport potential to surface waters, only groundwater transport potential. (We did add aquatic herbicide Endothall as an analyte at the request of early Chautauqua Lake volunteers.)
Long term groundwater sites waited until the third project year (2023) for selection, thus did not influence the analyte list developed in 2022. These have only a 15% quota for project samples, thus are a lower NYSDEC priority category than categorical sites and probably will not have much influence on revisions of the analyte candidate list.
As indicated in Figure 2, we next prioritized the candidate list based on use and sales popularity (focusing toward the generally more popular) and on the active ingredient properties that would make them spread more easily with water (less sorbing) and persist longer (slower degradation). There were 89 candidates that survived screening, around 20 from the combined categorical sites usage list and the rest from the older Cornell, Suffolk additions, and DEC nominees. For the 2022 samples, in early 2023 the NYSDEC lab tested initially for the new analytes for categorical sites and for DEC nominees, 28 analytes in total, then tested for the rest of the full analyte list during 2023. The lab tested for nearly all of the 89 analytes on the 2023 samples in January through May 2024. Samples are preserved well until analyzed via freezing.
Table 1 contains the 2022-2023 list with columns for the minimum and maximum lowest analytical detection limits in micrograms per liter, a field or typical soil degradation half life in days (t_{1/2}), a sorption parameter K_{oc} or K_{foc}, and a groundwater ubiquity score (GUS1). The latter column combines the half life and sorption parameter into an index that is higher when a chemical is more likely to move and persist until it reached groundwater, lower when it is less likely to move and persist. These two properties are from the Hertfordshire Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB2).
| parameter | pgroup | min_detlimit | max_detlimit | soil_halflife | HLtype | sorption | SORPtype | GUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,4-D | pesticides | <0.2 | <0.5 | 28.80 | field | 39.30 | koc | 3.82 |
| Acetamiprid | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.100 | 3.00 | field | 200.00 | koc | 0.94 |
| Acetochlor | pesticides | <0.25 | <0.25 | 12.10 | field | 156.00 | koc | 1.67 |
| Atrazine | pesticides | <*0.01 | <0.01 | 29.00 | field | 100.00 | koc | 2.57 |
| Azoxystrobin | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 180.70 | field | 589.00 | koc | 3.1 |
| Bentazon | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 7.50 | field | 55.30 | koc | 1.95 |
| Boscalid | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 254.00 | field | 772.00 | kfoc | 2.68 |
| Bromacil | pesticides | <*0.05 | <0.05 | 60.00 | typical | 32.00 | koc | 3.44 |
| Carbaryl | pesticides | <*0.05 | <0.05 | 16.00 | typical | 300.00 | koc | 2.02 |
| Chlorantraniliprole | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 204.00 | field | 362.00 | koc | 3.51 |
| Chlorpyrifos | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 27.60 | field | 5509.00 | koc | 0.58 |
| Chlorsulfuron | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 36.20 | field | 36.30 | kfoc | 3.80 |
| Clethodim | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 3.00 | field | 22.70 | kfoc | 1.26 |
| Clopyralid | pesticides | <0.2 | <0.5 | 11.00 | field | 5.00 | koc | 3.44 |
| Cloransulam-Methyl | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.1 | 10.00 | field | 30.00 | koc | 2.53 |
| Clothianidin | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.100 | 121.20 | field | 123.00 | koc | 3.74 |
| Cyantraniliprole | pesticides | <1.0 | <1.0 | 32.40 | field | 241.00 | koc | 2.59 |
| Cyprodynil | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.05 | 45.00 | field | 2277.00 | kfoc | 1.06 |
| Diazinon | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 18.40 | field | 609.00 | koc | 1.51 |
| Dicamba | pesticides | <0.2 | <0.5 | 3.90 | field | 5.28 | kfoc | 1.94 |
| Dichlobenil | pesticides | <10 | <10 | 5.40 | field | 257.00 | koc | 1.19 |
| Dichlorvos | pesticides | <2.5 | <2.5 | 2.00 | typical | 50.00 | koc | 0.69 |
| Difenconazole | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.5 | 91.80 | field | 3760.00 | kfoc | 0.83 |
| Dimethoate | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 7.20 | field | 28.40 | kfoc | 2.18 |
| Dinotefuran | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.100 | 75.00 | field | 26.00 | koc | 4.85 |
| Dithiopyr | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 39.00 | field | 801.00 | koc | 1.74 |
| Diuron | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 229.00 | field | 680.00 | koc | 2.65 |
| Endothall | pesticides | <2.5 | <2.5 | 7.00 | field | 85.00 | koc | 1.75 |
| Ethofumesate | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.05 | 37.80 | field | 118.00 | kfoc | 3.04 |
| Florpyrauxifen Benzyl | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.10 | 150.00 | typical | 32308.00 | koc | -0.76 |
| Fluazafop-p-butyl | pesticides | <0.25 | <0.25 | 8.20 | field | 3394.00 | koc | 0.43 |
| Fluazinam | pesticides | <0.1 | <0.10 | 25.90 | field | 16430.00 | koc | 1 |
| Flumioxazin | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.25 | 17.60 | field | 889.00 | koc | 1.31 |
| Fluopicolide | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 138.80 | field | 321.10 | kfoc | 3.2 |
| Fluopyram | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 118.80 | field | 278.90 | kfoc | 3.23 |
| Fluoxastrobin | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 52.60 | field | 848.00 | kfoc | 1.84 |
| Flutolanil | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 105.00 | field | 735.00 | kfoc | 2.29 |
| Fluxapyroxad | pesticides | <0.25 | <1.0 | 181.50 | field | 728.00 | kfoc | 2.57 |
| Fomesafen | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 86.00 | field | 50.00 | koc | 4.45 |
| Glyphosate | pesticides | <1.0 | <1.0 | 6.45 | field | 1424.00 | koc | 0.21 |
| Halosulfuron-methyl | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 14.00 | field | 109.00 | koc | 2.80 |
| Hexazinone | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 105.00 | typical | 54.00 | koc | 4.43 |
| Imidacloprid | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.05 | 174.00 | field | 225.00 | kfoc | 3.69 |
| Indaziflam | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 150.00 | typical | 1000.00 | koc | 2.18 |
| Iprodione | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 11.70 | field | 700.00 | koc | 0.43 |
| Linuron | pesticides | <0.25 | <0.5 | 48.00 | field | 842.80 | koc | 2.49 |
| MCPA | pesticides | <0.2 | <0.5 | 25.00 | field | 73.88 | koc | 2.31 |
| MCPP | pesticides | <0.2 | <0.5 | 21.00 | field | 59.80 | kfoc | 2.94 |
| Malathion | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | field | 1800.00 | koc | 0 |
| Mandipropamid | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 13.60 | field | 847.00 | kfoc | 1.22 |
| Mefentrifluconazole | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.05 | 200.00 | field | 3456.00 | kfoc | 1.06 |
| Mesotrione | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 5.00 | field | 122.00 | koc | 1.45 |
| Metalaxyl | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 14.10 | field | 162.00 | koc | 2.06 |
| Methiocarb | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 35.00 | field | 660.00 | kfoc | 1.82 |
| Methomyl | pesticides | <0.1 | <0.1 | 7.00 | typical | 72.00 | koc | 2.19 |
| Metolachlor | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 21.00 | field | 120.00 | koc | 2.36 |
| Metribuzin | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 19.00 | field | 48.30 | kfoc | 2.96 |
| Metsulfuron Methyl | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 13.30 | field | 12.00 | kfoc | 3.85 |
| Myclobutanil | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 35.00 | field | 517.00 | kfoc | 1.99 |
| Napropamide | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 72.00 | field | 839.00 | koc | 1.96 |
| Nicosulfuron | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 13.50 | field | 30.00 | koc | 3.44 |
| Oxadiazon | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.1 | 165.00 | field | 3200.00 | koc | 1.97 |
| Oxamyl | pesticides | <0.5 | <0.5 | 6.00 | field | 14.91 | koc | 2.23 |
| Paclobutrazol | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 29.50 | field | 400.00 | koc | 2.47 |
| Prometon | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 500.00 | typical | 43.20 | koc | 6.31 |
| Propamocarb HCL | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 20.00 | field | 706.00 | kfoc | 1.5 |
| Propiconazole | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 35.20 | field | 1086.00 | koc | 1.58 |
| Propoxur | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 28.00 | field | 30.00 | koc | 3.65 |
| Pyrimethanil | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 31.40 | field | 355.70 | kfoc | 2.17 |
| Quinclorac | pesticides | <0.05 | <0.05 | 450.00 | typical | 50.00 | koc | 6.29 |
| S-Metolachlor | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.05 | 23.17 | field | 0.00 | koc | 2.32 |
| Simazine | pesticides | <0.01 | <0.01 | 90.00 | field | 130.00 | koc | 2.20 |
| Sulfentrazone | pesticides | <0.25 | <0.25 | 541.00 | typical | 43.00 | koc | 6.16 |
| Tebuconazole | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 47.10 | field | 769.00 | kfoc | 1.86 |
| Tebuthiuron | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 400.00 | typical | 80.00 | koc | 5.36 |
| Terbacil | pesticides | <*0.5 | <0.5 | 115.00 | typical | 55.00 | koc | 4.70 |
| Thiamethoxam | pesticides | <*0.025 | <0.100 | 39.00 | field | 56.20 | koc | 3.58 |
| Thifensulfuron Methyl | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 10.00 | field | 28.30 | koc | 3.05 |
| Thiodicarb | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 18.00 | field | 418.00 | kfoc | 1.73 |
| Triadimefon | pesticides | <0.025 | <0.025 | 26.00 | typical | 300.00 | koc | 1.59 |
| AMPA | metabolites | <1.0 | <1.0 | 419.00 | field | 2002.00 | koc | 0.04 |
| Acetochlor ESA | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.05 | 90.00 | typical | 28.80 | koc | 3.73 |
| Acetochlor OA | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.05 | 12.00 | field | 24.30 | koc | 2.49 |
| De Ethyl Atrazine | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.25 | 45.00 | field | 110.00 | koc | 3.24 |
| De Isopropyl Atrazine | metabolites | <0.25 | <0.25 | - | 130.00 | koc | - | |
| Hydroxy Atrazine | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.25 | 164.00 | typical | - | - | |
| JSE76 | metabolites | <0.05 | <0.05 | 109.00 | typical | 30.00 | koc | 5.23 |
| Metolachlor ESA | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.15 | 400.00 | typical | 9.00 | koc | 7.22 |
| Metolachlor OA | metabolites | <*0.05 | <0.1 | 325.00 | typical | 17.00 | koc | 6.88 |
Navigate: ▲ 2: Sites and protocols
Last updated: 2024-12-17, sp17 AT cornell.edu
Footnotes
Gustafson, D. I. 1989. Groundwater ubiquity score: A simple method for assessing pesticide leachability. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 8(4), 339–357. URL: https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620080411 .↩︎
University of Hertfordshire, UK. 2024. Pesticide Properties Database. URL: https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/. Visited 2024-12-06.↩︎